pectus excavatum baby causes
While this can be noted early in life pediatric pectus excavatum often worsens during a growth spurt in adolescence. When should I worry about laryngomalacia.

Pectus Excavatum Ottawa Citizen
Decreased stamina compared to peers.
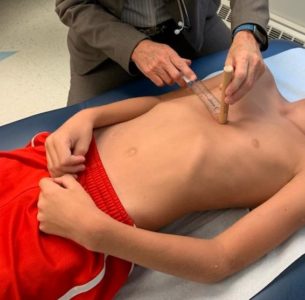
. The severity of this condition can range from mild to severe. The breastbone or sternum and some of the ribs grow abnormally causing a depression in the middle of the chest. Abstract Pectus excavatum PE is the most frequent anterior chest deformity occurring in approximately one of 1000 live births.
Pectus excavatum is usually congenital present at birth and can get worse during the early teenage years a time when bones grow rapidly. Pectus excavatum is caused by the abnormal growth in the chest of the connective tissues cartilage that attach the breastbone sternum to the ribs. The cartilage turns to bone as the baby matures.
The condition can be mild or severe. It makes up most of the skeleton as a baby develops before it is born. Ad Find information on chronic and acute pain its causes symptoms and recovery period.
Pectus excavatum can also be associated with connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome. Usually the ribs and sternum go outward at the front of the chest. Pectus excavatum is a congenital deformity of the chest wall that causes several ribs and the breastbone sternum to grow in an inward direction.
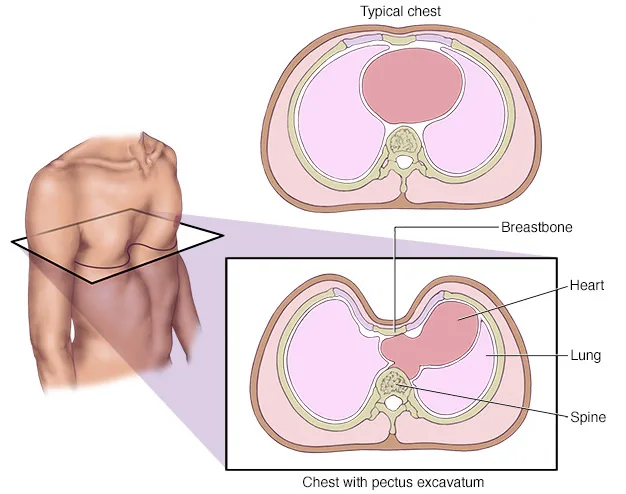
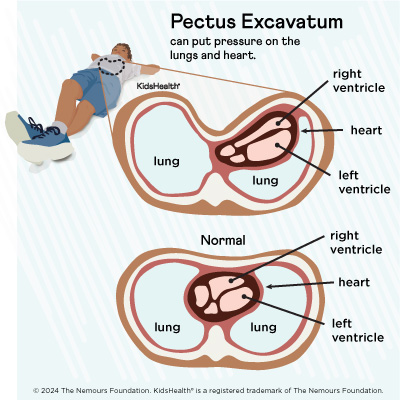
Shortness of breath with exercise. Poor posture with slumped shoulders and a protruding abdomen or pot belly Problems with bone growth and alignment later in life In severe cases PE shifts the heart to the left side of the chest and compresses the lungs limiting the childs ability to take deep breaths. Due to the pectus patients may have less space in the chest which can limit heart and lung function.
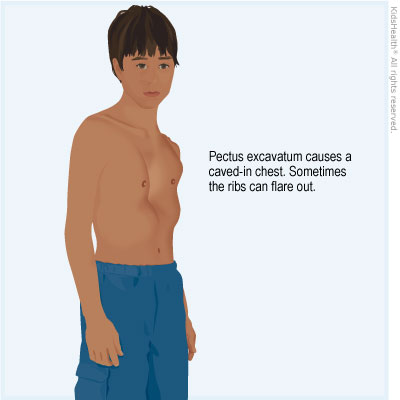
With pectus excavatum the sternum goes inward to form a. Pectus excavatum also known as concave chest or funnel chest is a deformity of your childs chest wall. Pectus excavatum is a relatively common congenital deformity a defect that is present at birth in which the chest appears sunken.
It is caused when several ribs and the sternum grow abnormally which produces a caved-in or sunken appearance of the chest. Find Information on Diseases Conditions Sports Injury Personal Injury. With pectus excavatum the sternum goes inward to form a.
It can also develop in a baby after birth. Symptoms and Causes What are the symptoms of pectus excavatum. Cartilage is a tough elastic fibrous tissue.
There is no known cause for pectus excavatum. Usually the ribs and sternum go outward at the front of the chest. The symptoms can be both physical and psychological.
It can sometimes run in families which suggests genetics may play a role. Pectus excavatum is due to too much growth of the connective tissue that joins the ribs to the breastbone. Pectus excavatum is a depression caused when the sternum breastbone is abnormally pushed inward.
Pectus excavatum occurs in approximately 1 out of 4001000 children and is three to five times more common in males than females. It is more common in boys than girls. The cartilage pushes the breastbone sternum inward.
The condition is sometimes called concave chest or funnel chest. Ad Dedicated to making research and biotech production simpler faster and safer. I was in junior high a time when your.
Despite the excellent achievements in the treatment of the disease the etiology of PE is yet to be clarified. This causes a depression in the chest that can range from mild to severe. Pectus excavatum is a condition in which the breastbone is sunken into the chest.
Pectus excavatum is a congenital deformity of the chest wall that causes several ribs and the breastbone sternum to grow in an inward direction. The deformity can become more visible as your child grows up especially during puberty. The cause of pectus excavatum is not known however it can run in families with up to 25 percent of affected patients reporting chest wall abnormalities in other family members.
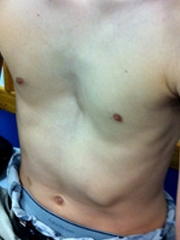
Both or just one side of the breastbone may be affected. Pectus excavatum is usually noticeable soon after birth. Physical symptoms can include.
Most common sign is slight indentation in the chestSymptoms that appear due to severe cases of pectus excavatum when the breast bone compresses the lungs or. It is believed that the cause for PE is an intrinsic costal cartilage abnormality leading to an. Call the doctor right away if your baby has these symptoms or breathing.
This is sometimes called sunken or funnel chest. The condition is not always noticeable at birth but is often apparent by the time a child is 2 to 3. Depending on the severity of the malformation PE may cause.
Pectus excavatum is caused by an overgrowth of cartilage as the chest wall is developing before birth. Ribcage problems do not usually cause problems when the heart and lungs are developing but rarely can affect how well they work in later childhood. Caused by the unstable positioning of the bars top at the underside of the sternum Lateral sliding owing to uneven pressure exerted on the bar on each side A shift of the bar due to stripping of supporting intercostal musculature Please be careful with your postoperative treatment.
At age 14 that he had the genetic condition known as pectus excavatum which causes the breastbone to sink into the chest sometimes dramatically. The depression in the chest is due to abnormal growth of the cartilage that attaches the sternum to the ribs. Pectus excavatum PECK-tuss ex-kuh-VAW-tum is a condition that causes a childs chest to look sunken or caved in It happens because of a defect in the tough connective tissue cartilage that holds the bony part of the ribs to the breastbone.
Power your next discovery with top quality products and technologies from SigmaAldrich. A child with pectus excavatum usually has a depression in the center of the chest over the breastbone which may appear quite deep. Pectus excavatum occurs in a baby who is developing in the womb.
Because of the deep depression the lower ribs can stick out and give the appearance of a potbelly in younger children. Pectus bar dislocation is categorized into three types. As the ribcage is more rigid than normal it can make it difficult to completely breathe out expire.
Chest Wall Disorder Pectus Excavatum For Parents Norton Children S

Pectus Excavatum Symptoms Treatments And Complications

Pectus Excavatum And Improve Your Homoeopathic Knowledge Facebook

Pectus Excavatum Ottawa Citizen

Should I Worry If My Child S Chest Is Sunken Cincinnati Children S Blog

Chest Wall Disorder Pectus Carinatum Johns Hopkins All Children S Hospital

Patient 2 Note Cafe Au Lait Spots Pectus Excavatum Widespaced Download Scientific Diagram
Pectus Excavatum Chest Wall Deformities Child Heart Specialist

Pdf Prenatal Diagnosis Of Pectus Excavatum

Kidshealth Pectus Excavatum Vacuum Bell Device Akron Children S Hospital
Pectus Excavatum Children S Hospital Of Philadelphia

Pectus Excavatum Funnel Chest Asthma Lung Uk

Pectus Excavatum Chest Wall Stanford Medicine Children S Health
Nuss Procedure For Pectus Excavatum Background Indications Contraindications
Chest Wall Disorder Pectus Excavatum For Parents Norton Children S

Strength Training With Pectus Excavatum Wasserman Strength

Pectus Excavatum Symptoms Treatments And Complications

Pectus Excavatum From A Pediatric Surgeon S Perspective Abstract Europe Pmc
